Getting Started - Webdriver.io
Follow this guide for a basic example of running a test with Webdriver.io Selenium bindings for Nodejs. For our example we will use a simple script that opens https://www.google.com.
Start by signing up and creating a new test case using the Create Test button on the dashboard.
Enter the test case name (e.g. Webdriver.io Demo) and press Next.
Scenario
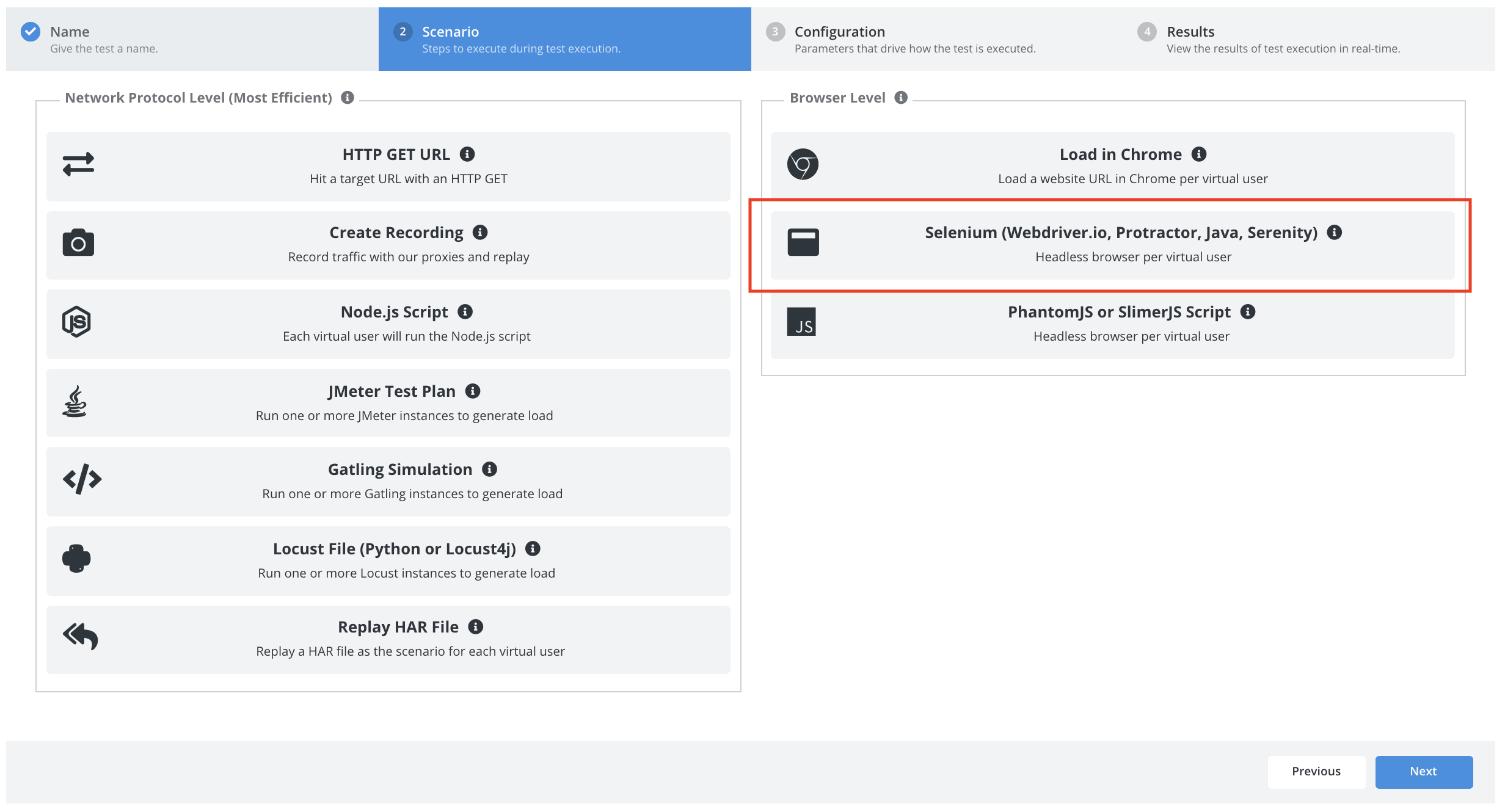
Select Selenium as the scenario type.
Let’s use the following settings:
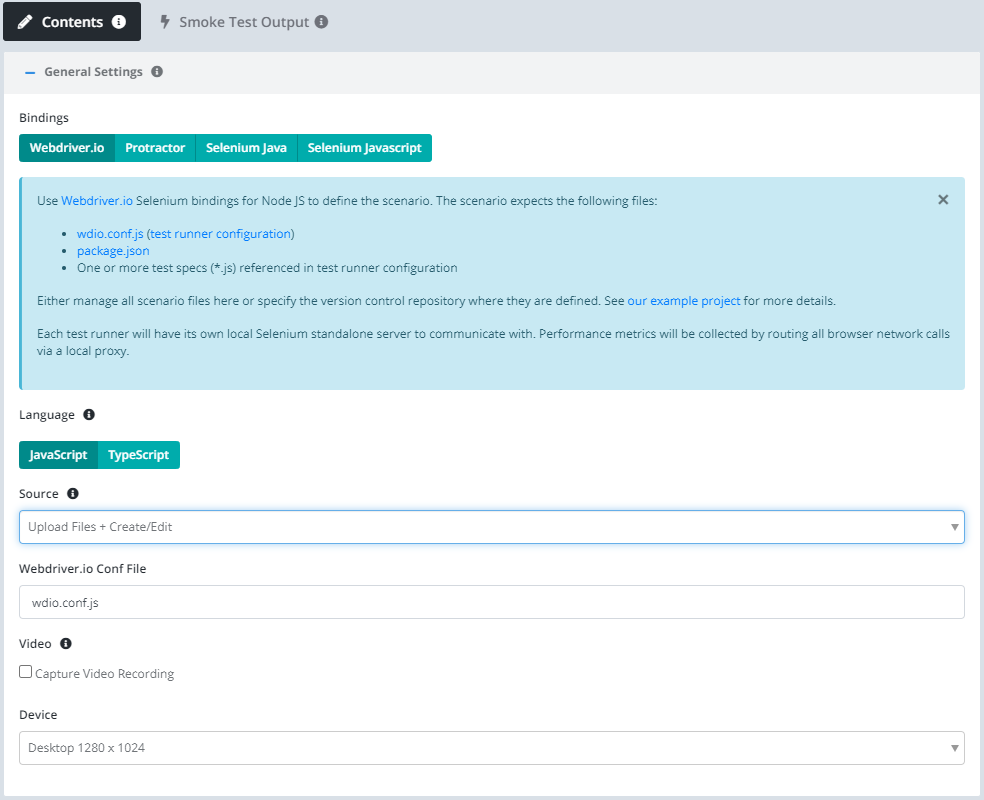
- Bindings: Webdriver.io.
- Run Style: Conf File
- Source: Upload. We can also connect our scenario to version control, but for now let’s just create the files in the browser.
- Language: Javascript
Next press the Generate Example button to generate an example project including a package.json, wdio.conf.js, and test.js file.
The default configuration file Testable provides uses Mocha as the testing framework and runs the test in Chrome. You are welcome to use other testing frameworks and capabilities as well.
Our example generated test spec:
const assert = require('assert');
describe('A basic test', function() {
it('should be possible to go to google', async function() {
await browser.url('https://www.google.com');
await browser.saveScreenshot('HomePage.png');
const title = await browser.getTitle();
assert.equal(title, 'Google');
});
});
And that’s it, we’ve now defined our scenario! To try it out before configuring a load test click the Smoke Test button in the upper right and watch Testable execute the scenario 1 time as 1 user.
Click on the Configuration tab or press the Next button at the bottom to move to the next step.
Configuration
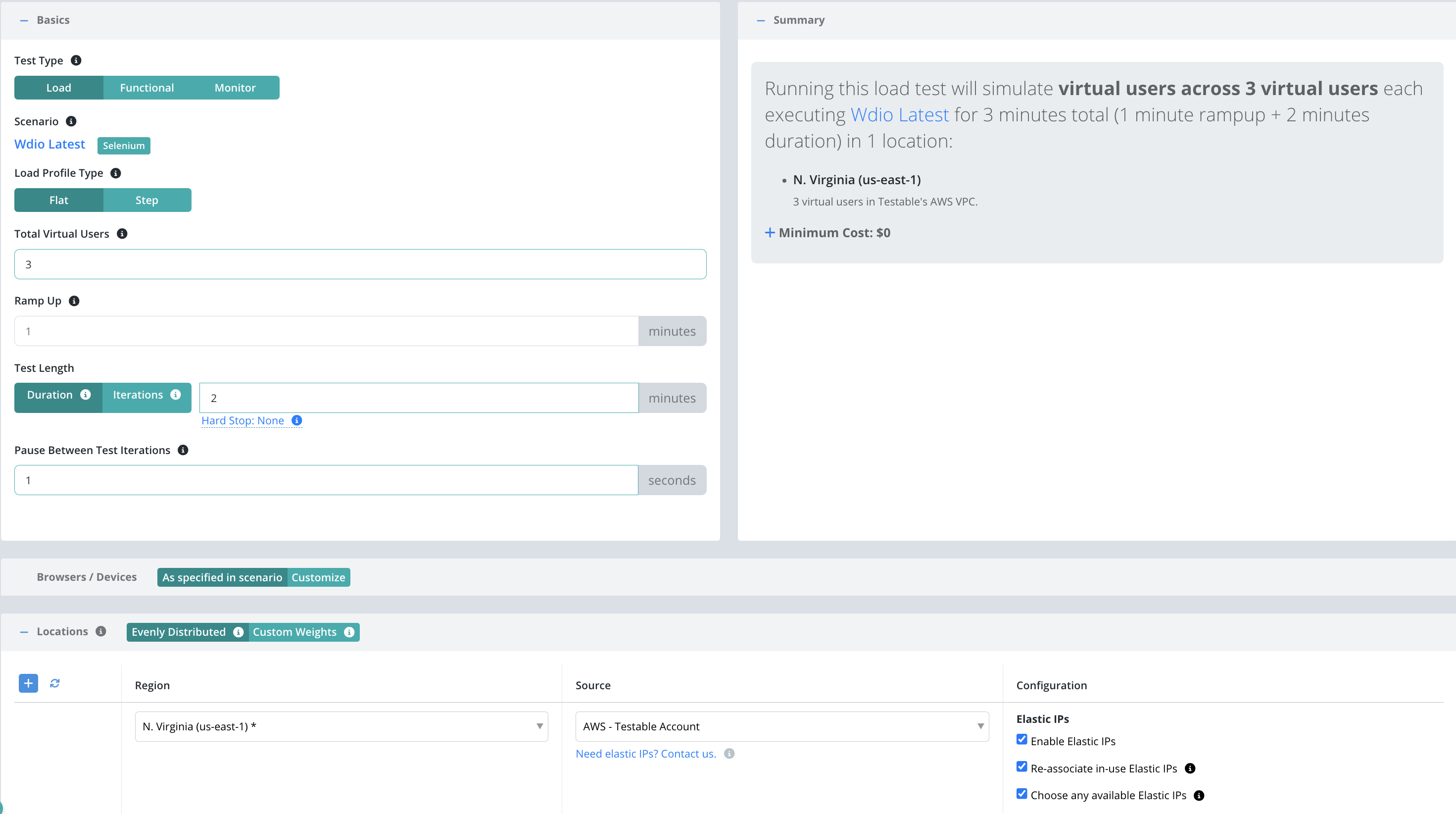
Now that we have the scenario for our test case we need to define a few parameters before we can execute our test:
- Total Virtual Users: Number of users that will execute in parallel. Each user will execute the scenario.
- Test Length: Select Iterations to have each client execute the scenario a set number of times regardless of how long it takes. Choose Duration if you want each client to continue executing the scenario for a set amount of time (in minutes).
- Location(s): Choose the location in which to run your test and the test runner source that indicates which test runners to use in that location to run the load test (e.g. on the public shared grid).
And that’s it! Press Start Test and watch the results start to flow in. See the new configuration guide for full details of all configuration options.
For the sake of this example, let’s use the following parameters:
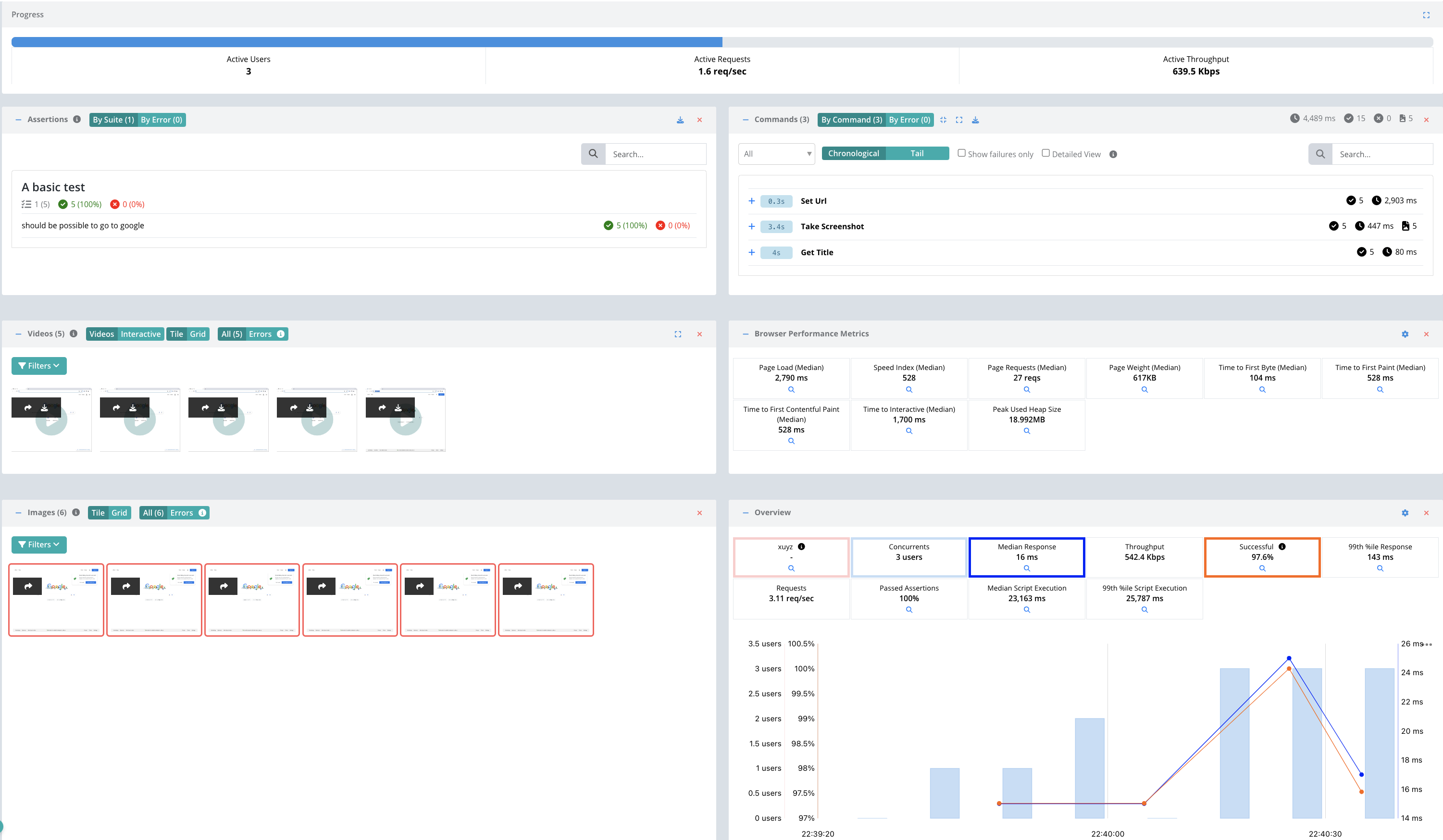
View Results
Once the test starts executing, Testable will distribute the work out to the selected test runners (e.g. Public Shared Grid in AWS N. Virginia).
In each region, the Testable runners execute the Webdriver.io script with 3 virtual users for 2 minutes. If the Webdriver.io test takes less than two minutes, it will sleep for 1 second and then run the test again until more than 2 minutes has passed.
The results will include videos, screenshots, assertions, traces, performance metrics, logging, breakdown by URL, analysis, comparison against previous test runs, and more.
Check out the Selenium guide for more details on running your Webdriver.io scripts on the Testable platform.
We also offer integration (Org Management -> Integration) with third party tools like New Relic. If you enable integration you can do more in depth analytics on your results there as well.
That’s it! Go ahead and try these same steps with your own scripts and feel free to contact us with any questions.